Whether you’re listening to music on your way to work or hearing the latest news updates while stuck in traffic, the radio is your best friend. Even with the advent of digital technologies, radio is far from dead. In fact, it continues to evolve.
Radios, however, can be confusing, especially for someone who lacks technical knowledge. Among others, two of the most common terms you’ll encounter are AM and FM. What does AM and FM stand for in radio?
If you’re clueless, read on and find out! Our concise explanation will save you from having to read long PDFs.
Table of Contents
AM and FM Definition and Evolution
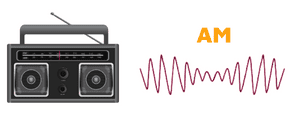
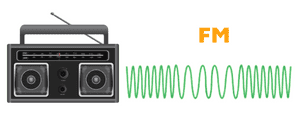
The AM radio abbreviation stands for Amplitude Modulation. Meanwhile, the FM acronym stands for Frequency Modulation. One of the similar characteristics they share is they both are artificially tuned signals for broadcasting. These radio signals are part of electromagnetic waves.
1. AM and its history
AM modifies a carrier wave for an input signal’s transmission. In this case, the input signal is the one carrying information. Most of these stations, also referred to as “medium wave” stations, are only for daytime. If they happen to operate at night, they will do so using low power; however, they must be authorized beforehand.
It was in the mid-1870s when AM was first utilized in radio via telephone lines. That said, it was not until the 1920s that AM broadcasting became popular. In the following 30 years, AM dominated the field of broadcasting, so much so that this period was dubbed the “Golden Age of Radio”. By the 1950s, radios were overtaken by televisions.
2. FM and its history
Meanwhile, FM is an encoding process wherein the frequency of the carrier wave changes depending on the modulating signal’s frequency. This is in contrast to AM, wherein it’s the carrier wave’s amplitude that changes.
Compared to AM, frequency modulation broadcasting is slightly newer, with its first transmission being in the 1930s. However, FM only became truly popular during the late 1960s due to its high-fidelity sound capabilities, which were highly sought after due to the increasing popularity of music over the airwaves.
Meanwhile, it’s also important to mention phase modulation or PM. In this case, the periodic carrier signal’s phase varies depending on the modulating signal.
Modulation
First, let’s describe what modulation is. In a nutshell, it is how radio waves are produced through data. Consequently, this is one of the defining characteristics when comparing AM vs FM.
Think of the carrier wave as a vehicle. It is where information is encoded. This carrier wave travels to the receiver, where it is accepted and demodulated.
In the case of AM, the modulation happens with varying amplitude. On the other hand, in the case of FM transmitter circuits diagrams, it is the frequency that varies during the transmission.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Now that you have an idea about the meaning of AM and FM, let’s briefly look at their benefits and drawbacks.
AM
- Advantages
Among others, a major benefit of AM is the simplicity of its circuits, which also makes it easy to control. Because it’s less complex, it requires fewer components. And that also brings us to how economical it is.
Lastly, it’s super effective because of its long range, allowing it to reach long distances. Compared to FM, AM boasts a much broader coverage, being able to reach thousands of miles away.
- Disadvantages
However, one of its shortcomings is its poor anti-noise interference, resulting in lower sound fidelity. And because AM relies on amplitude variance—the change in strength or height of radio waves, you’ll likely hear lots of static when changing stations.
FM
- Advantages
Its effectiveness in noise reduction is one of its biggest benefits. The main reason for this is that, unlike amplitudes, noises can’t interfere with a signal’s frequency. Similarly, nearby radio stations can’t affect FM’s transmission quality. As such, FMs can offer high-fidelity sound capabilities.
Another advantage is its bandwidth efficiency. As a result, it can transmit more information within its frequency range compared to AM.
- Disadvantages
One of the drawbacks of FM is that it costs more, which is partly due to its equipment requirements. Complexity aside, the high power consumption can also be a disadvantage.
A Comparison of AM and FM
Now, let’s take your knowledge of AM and FM a notch higher by looking at how they are different from each other. Here’s a quick rundown of their characteristics, followed by a table that will summarize the discussions.
1. Modulation
As mentioned above, it’s the amplitude that changes in the modulation of AM, and it’s the frequency that varies in the case of FM.
2. Sound Quality
One major difference between AM and FM is the quality of the sound they generate. This difference in audio quality is a result of the difference in encoding. This encoding manner makes FM less sensitive to interference, whereas AM can be affected by natural and artificial radio noises.
3. Range
In comparing amplitude modulation vs frequency modulation, another factor to look at is its range. The wavelength of radio waves is larger in AM than in FM. The reason for this is the lower frequency.
Meanwhile, larger wavelengths are known for conquering longer distances. As such, AM can travel longer distances while also demonstrating a better ability to get through solid objects.
4. Signal Strength
Earlier, we mentioned that FM sounds better than AM. One reason for this is that AM has weaker signals. The Federal Communications Commission rules that AM radio signals cannot go beyond 50 kilowatts.
5. Noise
This is also one thing that we can link to audio quality. AM is more susceptible to noise compared to FM. The varying frequency of FM makes noise less of a problem, which is also what makes the sound superior.
| Amplitude Modulation (AM) | Frequency Modulation (FM) | |
| History | The first transmission was in the 1870s.
Became popular in the 1920s onwards. |
First introduced in the 1930s and became popular in the late 1960s due to the demand for high-quality music. |
| Modulation | Varying amplitude during transmission | Varying frequency during transmission |
| Sound Quality | Poorer, more prone to interference, especially from nearby radios | Better, less prone to interference, virtually impervious to nearby radios. |
| Range | Longer | Shorter |
| Signal Strength | Weaker | Stronger |
| Noise | More vulnerable due to varying amplitude | Less vulnerable |
Which is Much Better to Use: AM or FM?
Which option to pick depends entirely on your preferences. Should you want a simple broadcasting system that can cover wide distances without insane power consumption, AM radios are a better choice.
However, for people who value sound quality and superior signal strength, FM radios triumph. This is especially useful for audiophiles who love listening to lossless audio.
FAQs
Why is AM radio used for talk shows and FM radio for music?
Audio quality is not as important in talk shows; hence, they are commonly broadcasted over AM.
On the other hand, FM is used for music because it has better audio quality, which makes the sound-listening experience better. The higher fidelity of FM allows it to broadcast sound frequencies better.
Can AM and FM radio signals interfere with each other?
There’s a chance, albeit incredibly low, that AM and FM can interfere with each other’s signals, but only when they are on the same frequency. However, this rarely happens, as AM and FM operate on different frequencies, with the former on 535 and 1605 kHz and the latter on 88 and 108 MHz.
In addition, even if the frequencies happen to overlap, FMs are usually impervious to interfering signals.
What is AM radio used for?
AM radio is used for long-distance communication. This is likely because of the inherent characteristics that allow it to reach longer distances than FM. More so, AM is used for communal broadcast, including news programs
Which frequency range is used by FM radios?
The range of FM’s frequency is higher than that of AM. It ranges from 88 MHz to 108 MHz. Switching from one station to another has a difference of 200 KHz. As for AM, its frequency range is 535 KHz to 1605 KHz, with a difference of 10 KHz in every station.
What are the similarities of FM and AM radio programs?
One of the similarities between the two is they both rely on radio signals, which is how broadcasting takes place. In addition, they both have their respective wave frequencies.
Conclusion
So, what does AM and FM stand for in radio? As noted, AM is for Amplitude Modulation, while FM is for Frequency Modulation. They represent two methods of broadcasting, but they are different in terms of their quality, range, and strength, among other things.
We hope this article clears things up for you. Should you have any relevant questions, feel free to comment below.

Hi, I am Amaro Frank – the Wind Up Radio’s content editor and writer. Working with Adam is so much fun, as his stories and experiences enrich my knowledge about radio communications and radio accessories. My main tasks in Wind Up Radio are building content and generating great articles on different topics around radio accessories.