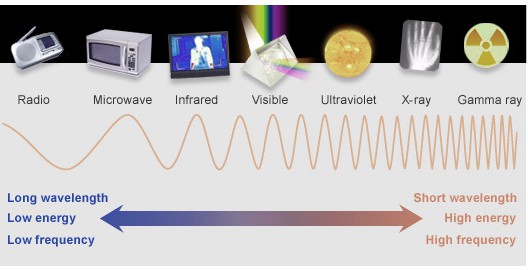
There are different types of electromagnetic waves. Radio wave, microwave, and infrared are the first three in the spectrum, followed by ultraviolet rays, x-rays, and gamma rays. In this post, however, our focus is in discussing the difference between radio wave and microwave.
Radio waves have a longer wavelength than microwaves. They are both used for communication, but radio waves are for longer distances compared to microwaves.
Read on to learn more about the most popular waves in the electromagnetic spectrum. We’ll start by discussing them individually and talk about their differences.
Table of Contents
All About Radio Wave
From car radio to air traffic control, radio waves are utilized in many ways. Here, we’ll share some things you need to know about radio waves.
1. What Is It?
Radio waves are at the lowest end of the electromagnetic spectrum. It has repeating wave patterns. A transmitter generates these waves, which the receiver detects. Between these two is an antenna acting as a bridge.
2. How Does It Work?
As earlier noted, several components are crucial for radio waves to work. Through such components, it’s possible to capture radio signals, which move quickly. It has frequencies that must be allocated efficiently.
It’s also available in different bands, which determine its frequency and wavelength.
3. What Is It Used For?
You might not realize it, but radio waves have tons of uses in our everyday lives, including the following:
- Radio communication
- TV broadcast
- Cellular networks
- Air traffic control
- Magnetic resonance imaging
- Remote-controlled cars
- Radio astronomy
- Travels very fast
- Low frequencies are not affected by line of sight
- Can be used in a wide range of frequencies
- Poor matter penetration
- Prone to interference from other radio waves
All About Microwave
When you hear about microwaves, most people will probably think about the kitchen appliance. However, while such makes sense, in this article, we are talking about the microwaves in the electromagnetic spectrum, just like radio waves.
1. What Is It?
Between radio waves and infrared radiation lies the microwave. If you look at the microwave science definition, you’ll see that it is an electromagnetic wave with a low frequency and long wavelength. They are available in varying wavelengths, which provide different information.
The frequencies can instantly send data when there are no obstacles, making microwaves good at transmitting information. The microwaves used for communication are the same waves you can use for cooking.
2. How Does It Work?
Microwaves can work in different ways, which will depend on their specific application.
For example, they reflect on metal surfaces. For such to happen, one of the most important components is a metal dish, which you can find in satellites. From here, information can be transmitted with the help of microwave radiation.
More so, water absorbs microwave frequencies. This is how it helps in cooking. Upon the absorption of microwaves, the food heats and cooks.
Lastly, it should be noted that microwaves can penetrate through plastic and glass. As such, these are the same microwave-safe materials. Therefore, you cannot put metal containers in the microwave.
3. What is It Used For?
One of the similarities between radio waves and microwaves is that they have almost the same uses. As such, below are some of the most common applications of microwaves.
- Cellular and satellite communication
- Radio astronomy
- Medical application
- Wi-Fi and Bluetooth
- Radar
- Cooking
- Has high frequencies that allow transfer of high quantities of information
- Low-cost transmission towers
- Good directive properties
- No need for a large antenna
- Only for line of sight communication
- Circuity design can be challenging
- Splits in solid objects
Microwave vs Radio Wave
Below is a more detailed radio waves and microwaves comparison, so you’ll better understand how one is different from the other.
Here’s a table for a quick summary followed by a short discussion of the differences between the two.
| Radio Wave | Microwave | |
| Wavelength | 1 m and above | 1 mm to 1 m |
| Frequency | 3 Hz to 300 GHz | 300 MHz to 300 GHz |
| Uses | Long-distance communication | Short-distance communication |
| Details | More detailed | Less detailed |
| Diffraction | Diffracts through obstacles | Goes in a straight line |
| Properties | Low frequency and energy | High frequency and energy |
1. Wavelength
One of the biggest differences between the two is their wavelength range. Looking at radio waves pictures, you’ll see they’re longer than the microwave’s wavelength. Take note that as the frequency increases, the wavelength decreases so they have an inverse relationship.
2. Frequency
The frequency of radio waves ranges from 3 Hz to 300 GHz. On the other hand, the frequency of microwave is anywhere from 300 MHz to 300 GHz.
It should be noted that microwaves are basically radio waves, but they have higher frequencies. Hence, you will find microwaves at the higher end of the electromagnetic spectrum.
3. Uses
As earlier mentioned, the two electromagnetic spectrums have similar applications. Among others, they are both used in communication. However, there is a slight difference as radio waves are for longer distances compared to microwaves.
4. Details
It should also be noted that microwave radar is more detailed than radio wave radar. The main reason for the latter is that compared to radio waves, microwaves have a smaller wavelength, making it more detailed.
5. Diffraction
One of the most important radio concepts is diffraction. It refers to bending around sharp objects, affecting how the signals reach the receiver.
Radio waves are known for their abilities to refract through obstacles. On the other hand, microwaves usually go in a straight line.
In addition, their diffraction is a great way to define how they travel. Radio waves are multi-directional and microwaves are unidirectional.
6. Properties
This is one thing that we can attribute to their position in the electromagnetic spectrum. Electromagnetic waves with shorter wavelengths also have shorter energy. And because radio waves have longer wavelengths, they have lower energy than microwaves.
Conclusion
In this post, we talked about the difference between radio wave and microwave. They are both parts of the electromagnetic spectrum but have slightly different characteristics.
Looking at an electromagnetic diagram or wave chart, radio waves are first and with the longest wavelength, followed by microwave. Despite their differences, the two have similar applications, especially when it comes to communication.

Hi, I am Amaro Frank – the Wind Up Radio’s content editor and writer. Working with Adam is so much fun, as his stories and experiences enrich my knowledge about radio communications and radio accessories. My main tasks in Wind Up Radio are building content and generating great articles on different topics around radio accessories.