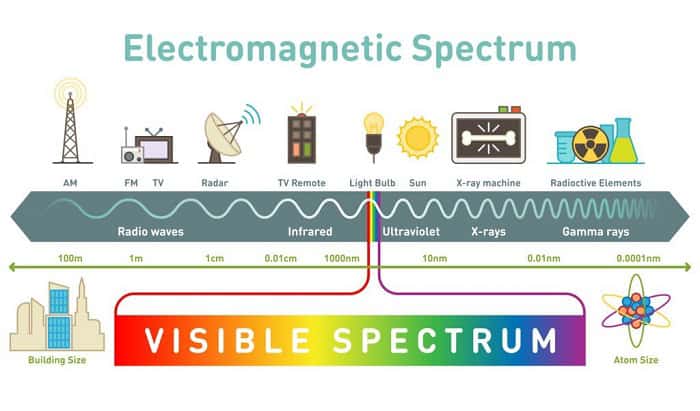
Visible light and radio waves are both parts of the electromagnetic spectrum. The latter is a collection of electromagnetic radiation in the universe. It exists in the form of magnetic and electric waves in the cosmos. They allow energy and information to transfer.
So, how does visible light compare to radio waves? They are different in terms of frequency, wavelength, energy, and visibility. Nonetheless, they are the same when it comes to speed.
It may seem quite technical, but in this article, we’ll keep things simple. Read on and find out the answer.
Table of Contents
What is the Electromagnetic Spectrum?
Before we talk about visible light and radio waves, let us first discuss the electromagnetic spectrum in general.
As soon as you turn on the TV, lamp, or radio, the electromagnetic spectrum transmits. Many of them are not visible, but they are important in science and in our daily lives.
In a nutshell, the electromagnetic spectrum collectively refers to electromagnetic radiation in the universe. It is a stream of photons traveling in a wave-like pattern.
The electromagnetic spectrum includes radio waves, visible light, microwaves, infrared, ultraviolet, gamma rays, and x-ray.
They all emit wavelength or frequency ranges. However, a main difference is that only visible light is visible to the naked eye.
How Does Visible Light Compare to Radio Waves?
Now that you have a rough overview of the electromagnetic spectrum in general, let us compare visible light and radio waves.
If you want to know more about the type of what other waves are present in an electromagnetic spectrum, this isn’t for you. Instead, it is specifically for comparing radio waves and visible light.
1. Visibility
One of the key differences between the two is their visibility. The name alone should already give you an idea. The only type of electromagnetic wave that is visible to the human wave is visible light.
Your eyes and brain will work together to convert visible light energy into electrical impulses that you can then interpret as an image. Your pupil, iris, and cornea are where the light enters until your brain processes them.
It is important to note that light makes up all of the electromagnetic radiation. Nonetheless, it is only visible light we can see. Others are too energetic and too small or too large for our biological limitations.
2. Speed
The speed of radio waves is the same as the speed of visible light. They are also the same as all the other types of electromagnetic waves. They will travel at the speed of light in a vacuum, which is 3 × 10 8 m s-1.
3. Frequency
One of the most important properties of electromagnetic waves is frequency. It is the number of waves passing at a time in a second. The basic measurement is Hertz, which is the number of cycles per second.
On average, radio waves have a frequency of 3 kilohertz to 300 gigahertz. The frequency of visible light depends on its color. For instance, the approximate frequency of blue light is 750 terahertz and 430 terahertz for the red light.
4. Wavelength
Visible light and radio waves do not differ only in frequency but also in wavelength. The latter is the distance from one’s wave peak to that of the next. A larger frequency will mean a shorter wavelength.
Because radio waves are at the spectrum’s beginning, they have longer wavelengths than visible light.
5. Energy
The energy in electromagnetic waves is referred to as radiant energy. It is the physical energy that results from radiation. The higher frequencies will carry more energy.
Do radio waves have more energy than visible light? Because radio waves are the first in the sequence it has the longest wavelength, which means that it has the lowest energy. So, to answer the question, radio waves have less energy than visible light.
Conclusion
So, how does visible light compare to radio waves?
In comparison to radio waves, visible light has better visibility. In fact, it is the only visible spectrum in an electromagnetic wave.
More than visibility, other key differences are that radio waves have a longer wavelength, which also means that it has lower energy. The shorter the wavelength is, the less is its energy.
Nonetheless, if they share a similarity, it would be that the two waves are both traveling at the speed of light.

Hi, I am Amaro Frank – the Wind Up Radio’s content editor and writer. Working with Adam is so much fun, as his stories and experiences enrich my knowledge about radio communications and radio accessories. My main tasks in Wind Up Radio are building content and generating great articles on different topics around radio accessories.